EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USIntroduction to Cisco SDWAN Security
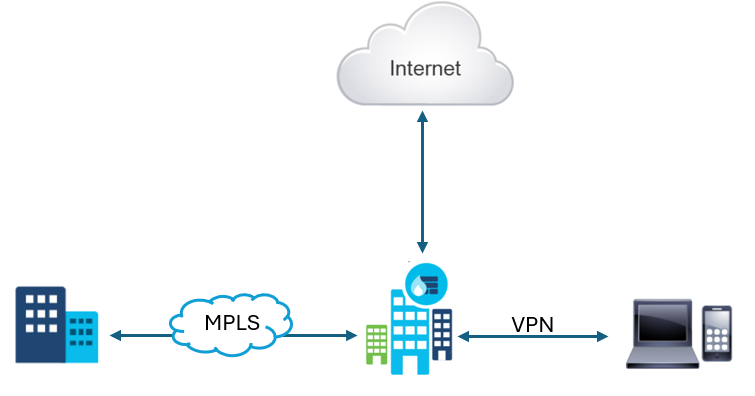
In Traditional WAN Security Approach and in traditional WAN architecture, most of the applications used by employees are hosted in a data center. That means that the bulk of the traffic flows occur between branch locations and the data center. To protect applications and users, a centralized security stack is positioned at the data center. These security solutions are often also found at the network perimeter to protect users and corporate data from any malicious activity originating from outside of the enterprise network.
However, with advancements in cloud technologies, and wider adoption of cloud-delivered services, traffic flows have changed, with more traffic now being destined to the internet. This means that backhauling all traffic through a centralized security stack is no longer efficient. Backhauling traffic in this way increases latency and can decrease the user’s overall quality of experience.
The centralized security approach can also prove to be complex and operationally cumbersome in large enterprise networks. Scaling can also become challenging, especially with fast growth, often requiring higher throughput on links and through security devices.
Traditionally, security components are deployed on-premises at the network perimeter to protect the enterprise network from any malicious activity that might come from the outside include:
- Stateful Firewall with Layer 4 capabilities.
- Application-Aware Firewall to facilitate application control.
- Intrusion detection system (IDS) or intrusion prevention system (IPS).
- Domain Name System (DNS) or Cisco URL Filtering to control web traffic, typically implemented in the form of a web proxy.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) decryption functionalities to decrypt encrypted traffic.
- Antimalware systems for further content control to filter any malicious attachments or file downloads.
- Sandboxing functionalities to inspect any unknown files or day 0 exploits.
Cisco Cloud Native Multi-Function Security Solutions
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) transforms enterprise security and networking. The widespread use of cloud apps, remote workers, and branch offices has made centralized on-premises security untenable. The convenience, cost savings, and performance benefits of direct internet access promote a new decentralized networking model. Change brings risks and new security issues. Organizations need a broader set of security and management tools.
Cisco Umbrella is a cloud-based security solution from Cisco that addresses today's business cases and security requirements.
Cisco Umbrella Cloud Security Overview
Cisco Umbrella provides cloud-based protection as needed. A single solution includes different security tasks to protect devices, remote users, and distributed locations. Umbrella protects your users worldwide in minutes.
Here are some of the cloud security functions Cisco Umbrella offers:
- DNS and web layer security blocks domains associated with malware, phishing, command, and control callbacks anywhere to stop threats at the earliest point.
- Secure web gateway provides content filtering by category or specific URLs to block destinations that violate policies or compliance regulations. It can scan all uploaded and downloaded files for malware and other threats using the Cisco Secure Endpoint (formerly Cisco Advanced Malware Protection [AMP]) engine.
- Cisco Secure Malware Analytics (formerly Threat Grid) to rapidly analyze suspicious files. It offers file type blocking (For example block download of .exe files) and full or selective SSL decryption to further protect the network from hidden attacks.
- Umbrella cloud-delivered firewall provides visibility and control for traffic that originated from requests going to the internet, across all ports and protocols.
- Ability to uncover cloud applications in use and block risky and unwanted apps and activities. Specifically, core technology from Cisco Cloud lock (the Cisco Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) solution) has been built into Umbrella to help expose shadow IT by providing the ability to detect and report on the cloud applications that are in use across the network.
- Security researchers constantly analyze DNS usage information and supplement it with intelligence from Cisco Talos to uncover malicious domains, IPs, and URLs before they’re used in attacks.
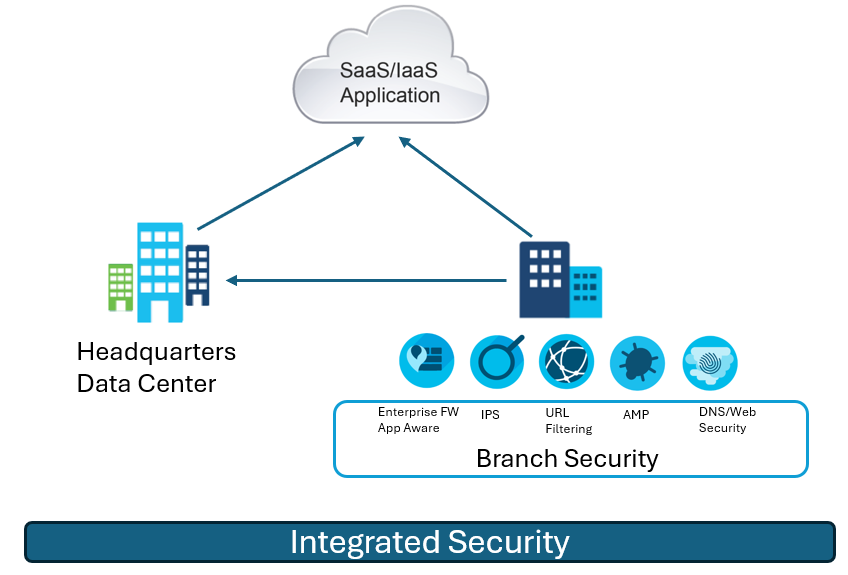
Integrated Security Deployment Model
Integrated on-premises security is when all security functions run on the Cisco SD-WAN Edge device. It is often referred to as a thick branch and is a single platform for routing and branch security at the branch.
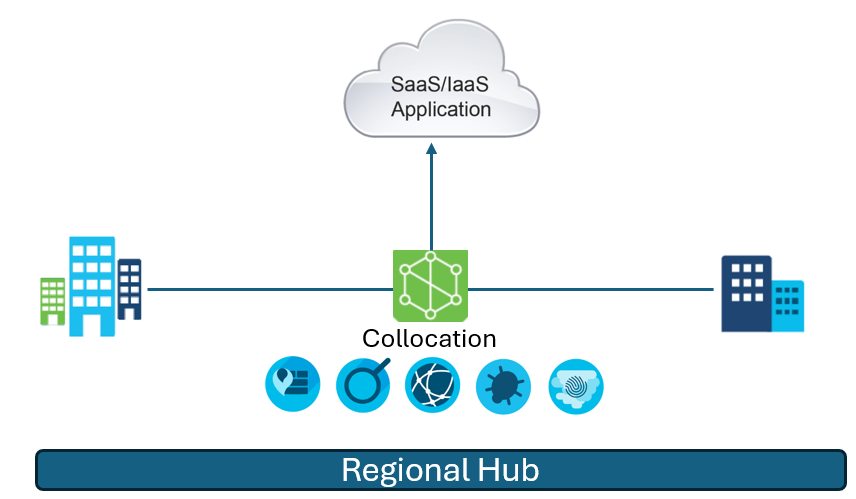
Regional Hub Deployment Model
Regional hub deployment uses service chaining, with dedicated security devices or VNFs hosted at a regional hub. This deployment model applies a thick branch approach for routing at the branch, but the security services are located at the regional hub.
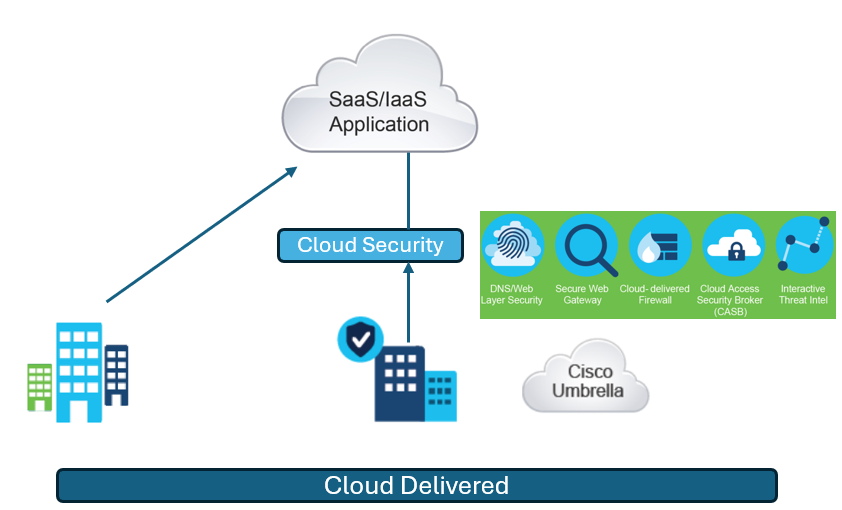
Cloud Security Deployment Model
Cloud-delivered security is also referred to as a thin or lean branch. This type of branch uses the cloud to deliver the necessary security solutions it needs. In this example, Cisco Umbrella can provide DNS-layer security, secure web gateway services, a cloud-delivered firewall, CASB functions, and interactive threat intelligence reporting.




LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.