EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USDeploy Service Chaining
When deploying service chaining, there are certain design considerations. Services are connected to Cisco SD-WAN Edge devices. The connection may be One-Arm or a Two-Arm, and depending on the deployment each option brings certain benefits and drawbacks. You should configure the services to forward traffic appropriately and you should configure security policies for the services to perform their function.
The services must be advertised into the fabric. Cisco SD-WAN Edge devices that the services are connected to are responsible for the advertisement of the service. The IP address of the service must be locally resolvable to advertise the service to the vSmart controllers.
The administrator must define a policy to route certain traffic flow to the available services. If there are multiple chained services (service chaining), then you must define additional policies to successfully route the traffic from the source, through several services, to the destination.
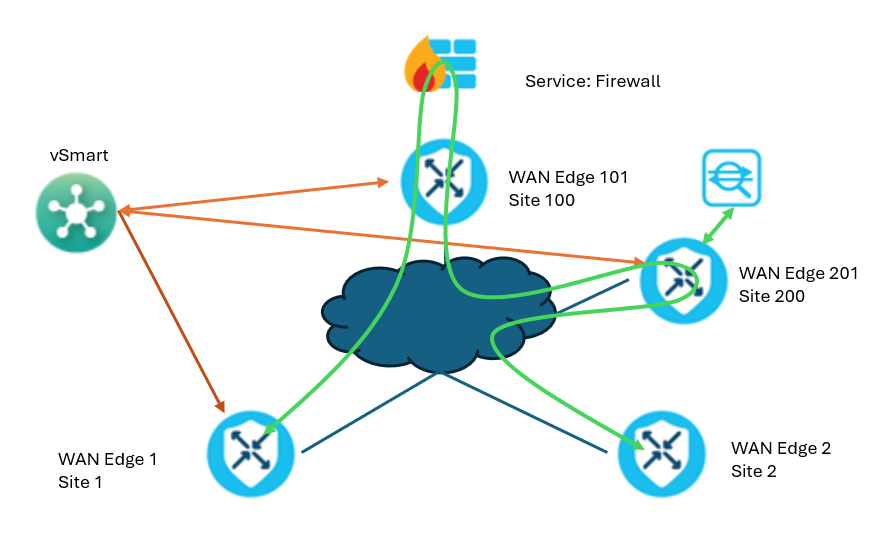
Advertising Services
Cisco SD-WAN Edge devices advertise the services configured within the VPN templates to the vSmart controllers. Each VPN can contain up to seven services. The routers advertise each service individually per VPN only to the vSmart controllers. The routers never advertise services to each other.
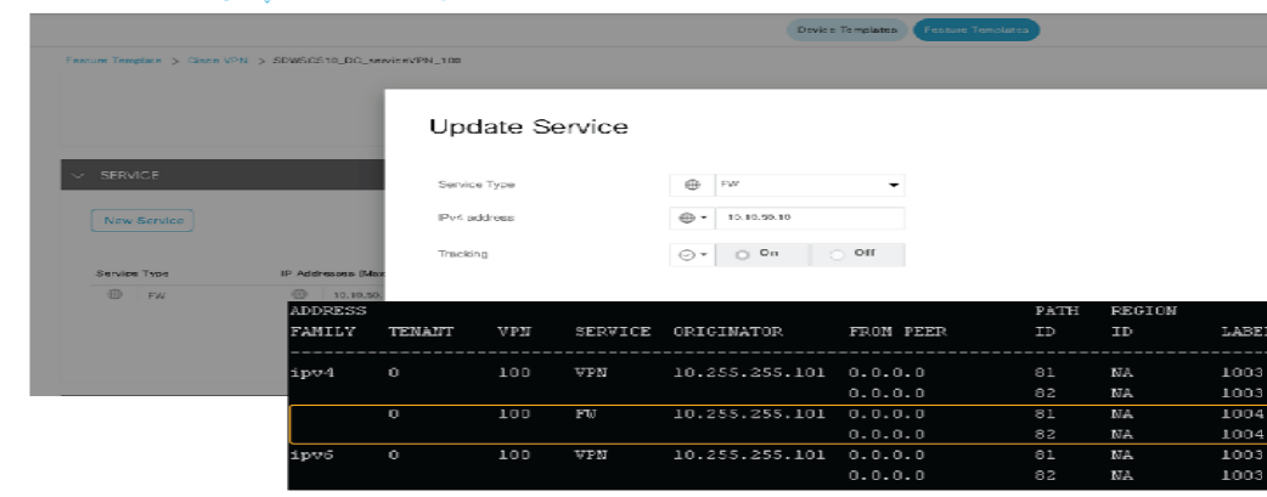
For a successful advertisement of service, the IP address of the service must be locally resolvable and reachable by the Cisco SD-WAN Edge device. Beginning with Cisco IOS XE Release 17.3.1a, Cisco SD-WAN periodically probes devices providing network services to test whether they are operational. Tracking the availability of devices in the service chain helps to prevent a null route, which can occur if a policy routes traffic to a service device that is not available.
Service Chaining with Control Policies
A centralized control policy is used to define the network topology.
When using control policies to deploy service chaining, the policy is applied networkwide across the selected sites. The vSmart controller enforces the control policy by essentially changing the next hop for a certain route. This means that the service receives all traffic from the sites the policy applies to, based on the prefix defined in the policy. Control policies match the control plane parameters, such as Prefix Lists, sites, Community Lists, and other control plane parameters.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.