EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USIntroduction to Cloud Onramp for SaaS
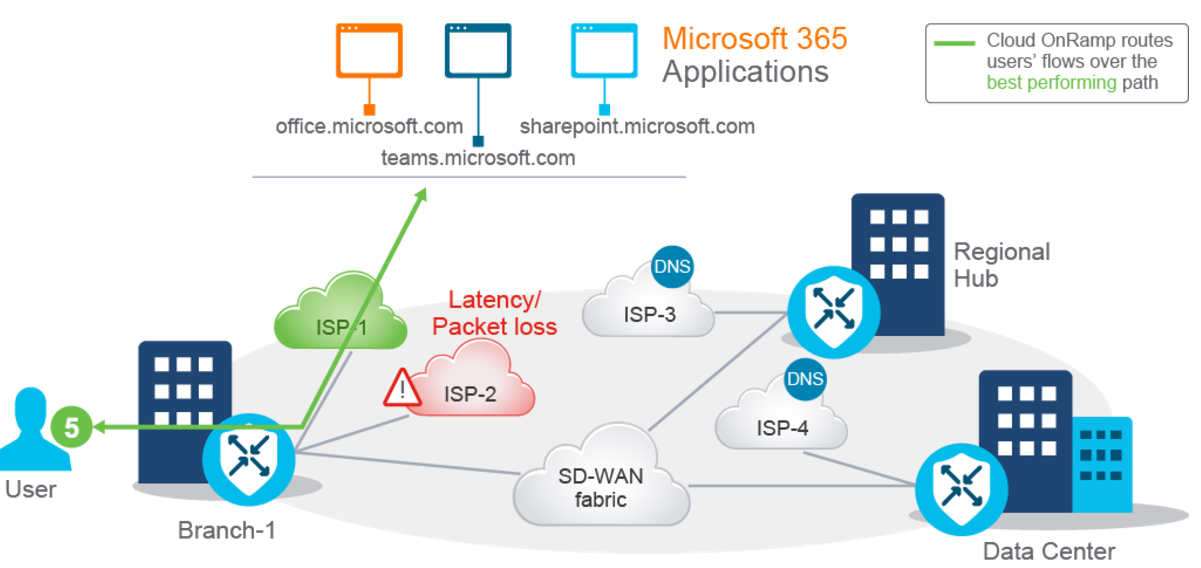
Cloud OnRamp allows only predefined applications to break out to the internet through the specified local DIA circuits while determining the best-performing path for each SaaS application.
- Cloud OnRamp continuously monitors each available path for each SaaS application.
- If there is a problem with one path, Cloud OnRamp dynamically moves the SaaS traffic to an alternative one.
- There are a few common architectures (scenarios) for access to SaaS applications:
-
- Accessing SaaS applications through DIA Links at branches
- Using the DIA link of a Gateway Site for redundancy
- DIA through Colos or CNFs
There are many benefits of Cloud OnRamp for SaaS, including:
- Improved branch-Microsoft user experience for SaaS applications by using the best-performing network path.
- Increased SaaS application resiliency with multiple network path selections and active monitoring.
- Visibility into SaaS application performance by using probes that measure real-time data.
- Modification of path selection depending on the application performance without any required administrator action.
- Operational simplicity and consistency through centralized control and management of SaaS application policies.
Accessing SaaS Applications Through DIA Links at Branches
You can use multiple inexpensive internet links at remote branches to enable Cloud OnRamp on the WAN Edge router. In this manner, you can permit traffic from selected SaaS applications to break out directly to the internet. It is important to note that only traffic from these SaaS applications can use the local internet links, while all other user traffic follows the regular overlay routing paths.
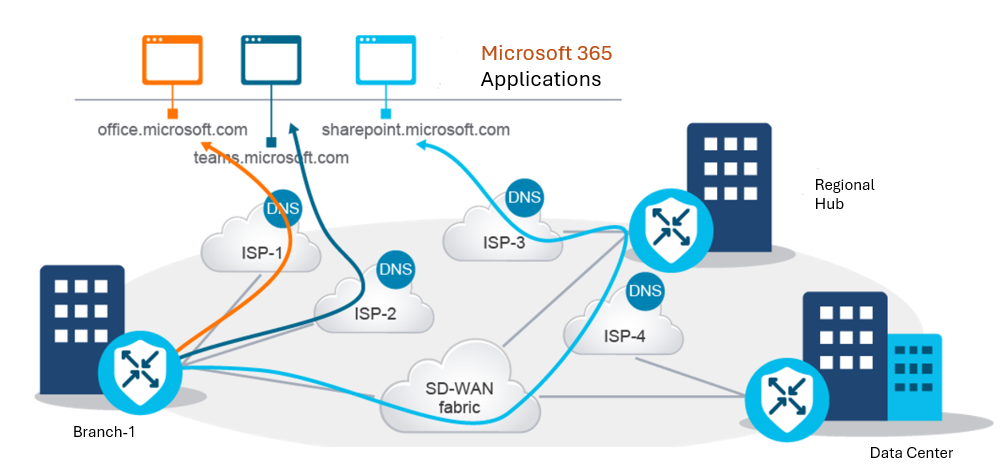
The below figure Cloud OnRamp for SaaS Quality Probing shows that you can specify a SaaS application for Branch-1.
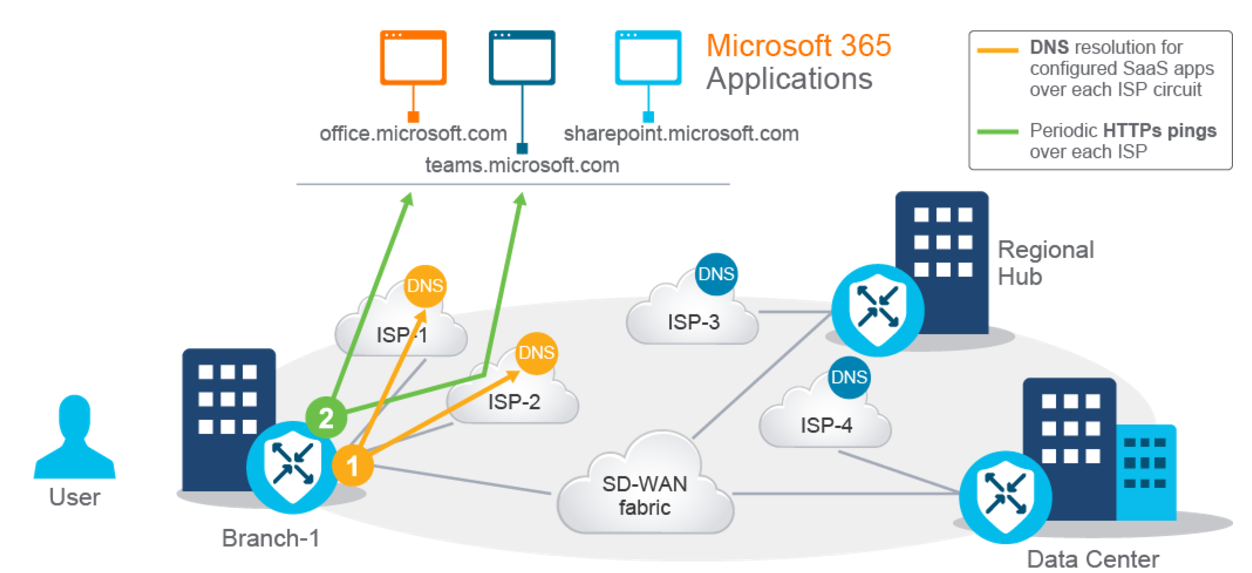
In that case, the Cisco SD-WAN Edge on-site performs these steps:
-
The WAN Edge router at Branch-1 performs Domain Name System (DNS) resolution for the configured SaaS applications separately over each Internet service provider (ISP) circuit. This implies that there must be a DNS server address in VPN 0 for each different ISP. The most popular SaaS applications have their worldwide networks and resolve with different IP addresses in different regions and subregions of the world.
-
The WAN Edge router at Branch-1 initiates periodic HTTP pings to each configured SaaS application. This activity is done separately over each ISP circuit. Based on the HTTP pings' packet loss and latency values, the QoE score (1-10) calculates. The WAN Edge router chooses the path with the highest score as the best-performing path.
The Below figure Cloud OnRamp for SaaS Host DNS resolution depicts a chain of events that happens when a user onsite connects for the first time to one of the SaaS applications.
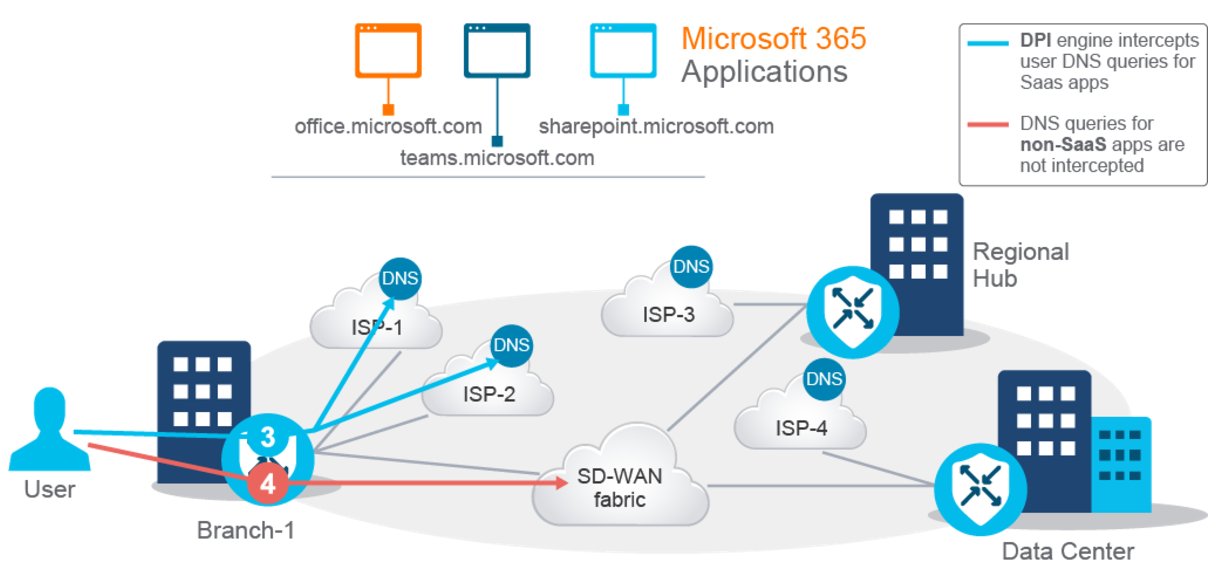
Your device generates a DNS query for the applications' URL and initiates these steps:
-
The WAN edge router's deep packet inspection (DPI) engine intercepts your DNS query. If the host DNS query is for the Cloud OnRamp SaaS application, the vEdge router forwards it over the best-performing circuit to the DNS server defined for this ISP.
-
DNS queries for non-Cloud OnRamp applications forward according to the routing table towards the Cisco SD-WAN overlay fabric.
Using DIA Link of Gateway Site
In many deployments, remote sites only have one internet link for DIA. In this case, the remote site tunnels SaaS traffic to a gateway location, and then uses the internet at the gateway location to access the SaaS applications. So, the remote site can use a gateway site that has DIA links to the internet for redundancy in case its own internet link degrades.
If the remote site connects to more than one gateway site, Cisco SD-WAN ensures that SaaS traffic uses the optimal path for each application, even through different gateway sites.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.