EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USLocator ID Separation Protocol
LISP is Location ID separation Protocol which acts as overlay for Intelligent branch Solution while implementing SD-Access.
It is very much used in SD-Access, providing overlay solution for SD-Access fabric. This LISP course will enable to learn about LISP Architecture, LISP Control Plane & data Plane, LISP traffic Flow and LISP Host mobility solution. This is the best LISP trainig course or LISP Training provides you very deep-dive concept of every topic along with CLI command line example and also helps you to understand Configure & Troubleshoot LISP Protocol.
This LISP training also contains best Cisco LISP lab configuration in all major concepts , Configuration are well written and tested as per Cisco LISP lab standard.
Course Pedagogy:
The Course Pedagogy will help you to learn the following concepts on Configure & Troubleshoot LISP Protocol on Cisco Nexus 7000 series Switches Hardware Platform.
- LISP Architecture
- LISP Control & Data Plane Fundamentals
- LISP Host Mobility Solution
- LISP Host mobility with Extended subnet
- LISP Host Mobility across Subnet.
LISP is said to be Locator/ID Separation Protocol, which enables separation of Location of End points and its identity while sending the traffic. LISP can be used as Overlay protocol for SD-Access branch network.
There are two namespaces which LISP uses in it operation:
- Identity Namespaces
- Location Name Spaces
Identity Namespaces:
Each endpoints network host in LISP is allocated with a unique identity or address to identify endpoints from each other in Identify Namespace called as EID namespaces. It can be looked like person name, which don’t have enough information to send traffic to destination but is used to find the desired location of Network host.
Location Namespaces:
Network devices to which host are connected are assigned address in Location namespaces. It can be looked like building are assigned a street address, this Location Namespace in LISP is also treated as routing locator (RLOC) namespaces. These address in RLOC are fully routable and all those network devices in RLOC namespaces are involved in sending data traffic to each other.
LISP protocol manages database which contains Identity and Location name space are mapped each other.
LISP Protocol is Overlay protocol which has two plane used to send data traffic successfully from source to destination. These two plane on any Overlay services are as follows:
- Virtual network in Overlay plane.
- Transport network in underlay plane.
This can be very well understood by below diagram
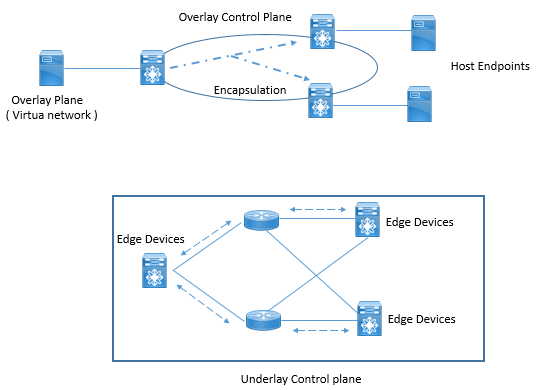
Underlay plane is traditional network consist of Switches , Router running switching and routing protocols to provide reachability between each other or each other sites. This plane does not information about end points connected to network. In LISP term Underlay plane handles routing only between RLOC address.
Overlay plane is a virtual network service which runs on top of underlay network, when traffic is send between hosts, it is tunneled between Network Edge devices via underlay network. To tunnel host traffic, edge device must know to which Network edge the destination host is connected to and this can be achieved by Location and Identity namespace. The process of mapping identity to location so that traffic can be encapsulated to destination location is called as map & Encapsulate.
LISP basically runs between edge of network, and these LISP edge routers are called as tunnel routers and its role is determined by direction of traffic, when the traffic is at ingress it is called as Ingress tunnel Router (ITR) and when traffic is egress from LISP overlay it is said as Egress Tunnel Router (ETR).
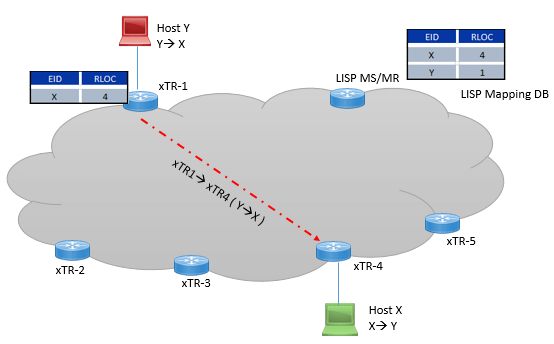
To be on more specific side, an ITR encapsulate the EID traffic and tunnel it, transport it over RLOC underlay, in term of packet header, the inner header will be EID name space and outer header will be RLOC name space.
The resolution of Host EID name space to Location name Space is just like or similar to DNS resolution.
ITR does not have any local copy of mapping of all EID that wants to send traffic, instead when ITR receives the any traffic for particular destination EID, it request the mapping of destination EID and its location from LISP Mapping database system, When request is received by LISP mapping database system, it replies specific mapping to ITR and then ITR encapsulate and forward traffic over LISP overlay tunnel and cache this information to its local Mapping database table.
In local mapping database, EID can be single host or entire EID prefix. Following figure explains what we have learned above.
Note: ( Refer before Purchase )
- We don't offer Any Hands-On labs for practice in this course.
- Lab discussed here contains different Scenarios, task & Its recorded Solutions.
- Content of each page is 30-40% visible for Customer verification about content.
- Before any purchase , verify content then proceed,VLT is in progress,No refund Policy.
- For More Detail : Mail dclessons@dclessons.com , FAQ & TC page.




LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.