EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USComparing DNS Layer Security and Cisco URL Filtering
DNS filtering and Cisco URL Filtering perform similar functions. The main difference is that Cisco URL Filtering blocks HTTP or HTTPS requests, while DNS filtering blocks DNS queries. Another way to put it is that Cisco URL Filtering blocks web pages, while DNS filtering blocks domains.
DNS filtering makes it possible to block a website and all its web pages, no matter their URLs, by blocking the domain name. However, Cisco URL Filtering provides more granular and detailed filtering by allowing companies to block individual web pages instead of the whole website at once.
Because Cisco URL Filtering is more granular than DNS filtering, it may also require more maintenance and customization. The network administrator will implement Cisco URL Filtering separately for each application protocol. By contrast, DNS filtering is protocol-agnostic, which means it applies to all types of traffic once enabled.
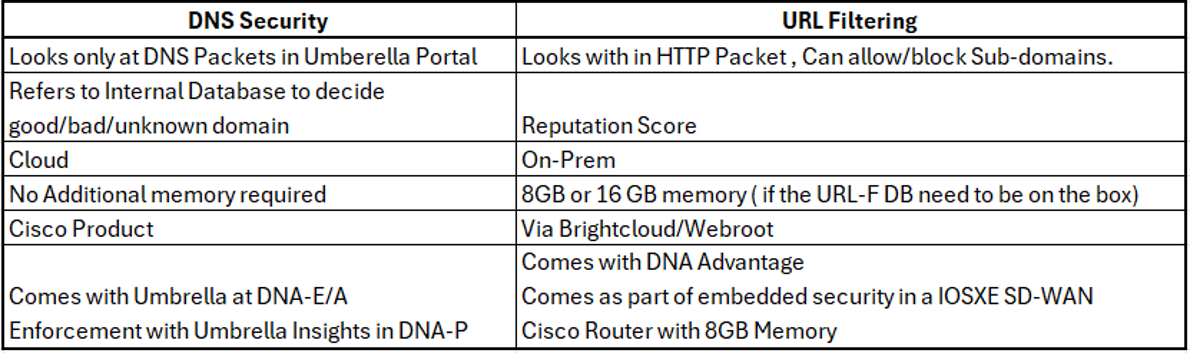
DNS Security refers to its internal database to decide if a domain is good, bad, or unknown.
DNS Security requires no additional RAM, but Cisco URL Filtering requires 8GB or 16GB. DNS Security is a Cisco product, while Cisco URL Filtering uses Webroot and Brightcloud. DNA-E/A includes Umbrella, and the DNA Advantage includes Cisco URL Filtering.
Cisco URL Filtering—Filtering Options
Cisco URL Filtering allows a network administrator to filter traffic by using these options:
- Category-based filtering
- Reputation-based filtering
- List-based filtering
Category-Based Filtering
A network administrator can classify URLs into multiple categories, such as News, Social Networking, Education, Adult, and so on. The user can either block or allow one or more categories based on the requirements.
There are up to five URL categorization types, and the system will block the request if it matches a blocked category.
Reputation-Based Filtering
In addition to category-based filtering, it is possible to filter based on the reputation of the URL. Each URL has a reputation score associated with it. The reputation score range is from 0 to 100.
Here is a list of vManage reputation scores:
- High risk: Reputation score of 0 to 20.
- Suspicious: Reputation score of 21 to 40.
- Moderate risk: Reputation score of 41 to 60.
- Low risk: Reputation score of 61 to 80.
- Trustworthy: Reputation score of 81 to 100.
A reputation threshold is defined when a network administrator configures a web reputation in vManage. Cisco URL Filtering blocks any URL that is below the threshold. For example, set the vManage web reputation setting to Moderate Risk to block access to any URL with a reputation score of 60 or less. vManage will block or allow URLs based on the reputation score and the configuration.
List-Based Filtering
List-based filtering allows users to control access by permitting or denying access based on allowed or blocked lists.
Here are some essential points to note regarding these lists:
- The new configuration will not override the initial one if the network administrator allows the set of URLs and adds more category-based filtering policies afterward.
- Traffic is allowed if the network administrator specifies identical items in both the allowed and blocked lists.
- Some lists allow or block URLs. If the traffic does not fit into any of the lists, the category and reputation-based filters will analyze it and, if required, filter it.
- A user may consider using a combination of allowed and blocked pattern lists to design the filters. For example, if you want to allow www.foo.com but also want to block other URLs, such as www.foo.abc and www.foo.xyz, you can configure www.foo.com in the allowed list and www.foo. in the blocked list.
Here is a simple order of operation with Cisco URL Filtering:
- A user from the Branch initiates a connection to an application on the internet.
- A router or firewall will redirect traffic to the Cisco URL Filtering engine.
- The connection is allowed or blocked based on the configured policy.
- The user is redirected to a block page if the connection is blocked.
- The user is directed to the original destination if the connection is allowed.
Cisco URL Filtering—Database Overview
By default, WAN Edge Routers do not download the URL database from the cloud.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.