EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USSecuring Cloud Application with Cisco Umbrella - Introduction
Cloud Application Security Overview
Traditionally, organizations routed internet traffic from branch offices back to a central location to apply security. Yet, this centralized security approach has become impractical in today's branch offices with high cloud application use due to the performance limitations of backhauling traffic.
You must adopt a new approach for cloud security and solution such as a SIG to:
- Improve security coverage.
- Centralize (consistent) policies across remote locations.
- Achieve better performance and user satisfaction.
SASE combines networking and security functions in the cloud to deliver secure access to applications anywhere users work. The core functions include Cisco Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN), firewall as a service, secure web gateway, Cisco Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and Zero Trust network access (ZTNA).
SASE helps organizations to:
- Combine networking and security functions to deliver secure connectivity as a service.
- Connect users seamlessly to the applications and data in any environment and from any location.
- Control access and enforce the proper security protection at any workplace.
Cloud Governance Policies
Implement the best security-related practices in cloud governance policies to:
- Enforce authentication standards.
- Establish hardening standards for virtual machines, containers, and approved repositories.
- Include strong access management: clearly defined roles and rules (for example, who has access to what and why).
Cloud Data Protection
Cloud computing allows the sharing of folders and files among multiple users. IT network security teams must be proactive in enabling the right cloud security policies around file sharing and sensitive data.
To be proactive, security engineers can take these actions:
- Identify sensitive data: Network security teams must plan which data or application access management is required. Sensitive data includes customer data, organizational policies, and other information, such as keys and hardcoded passwords. Sensitive data requires protection, and it would be great to store it in a separate folder with limited access.
- Categorize and protect files: Categorize data in a different section and apply encryption or other protective mechanisms to ensure that only the intended audience can view it.
Real-Time Session Controls
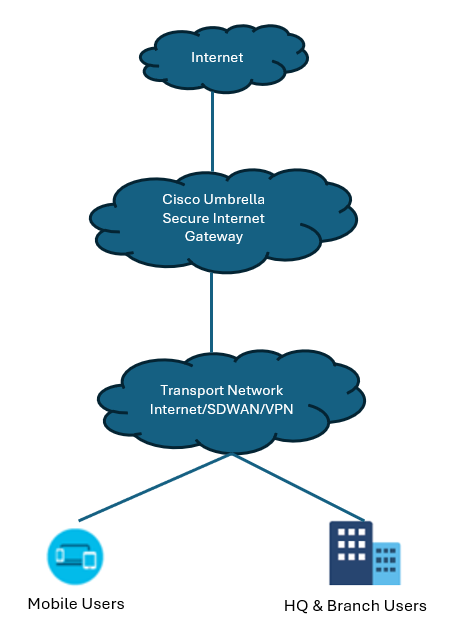
A network administrator can create a session policy to improve visibility and ensure secure collaboration in the cloud environment. The session policy enables tracking each session between internal and external users and, more importantly, limit specific activities against application security and compliance standards.
It is possible to monitor potentially risky or suspicious users when they sign into applications and log their actions into the session. The network administrator can further evaluate these session logs and analyze user behavior to detect violations of its security policies.
Malware Threat Protection
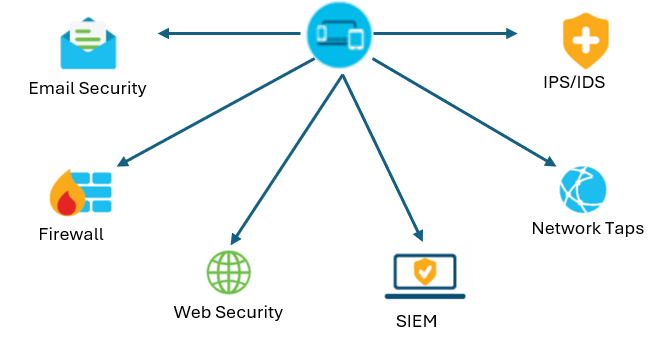
To address malware threats in the cloud, consider these application security activities:
- Organizations should stack up endpoint protection to the highest application security standards possible. This approach will help network administrators to detect most malware coming from endpoints, such as laptops and desktops.
- Create a BYOD protection policy to ensure secure upload and download of files from unmanaged endpoints.
- Ensure the use of advanced threat protection tools and processes to limit the spread of malware to other networks in the enterprise.
- Add a cloud-specific protective layer to all cloud-based email applications to secure infrastructure hosted on Gmail or Microsoft.
DNS Layer Security
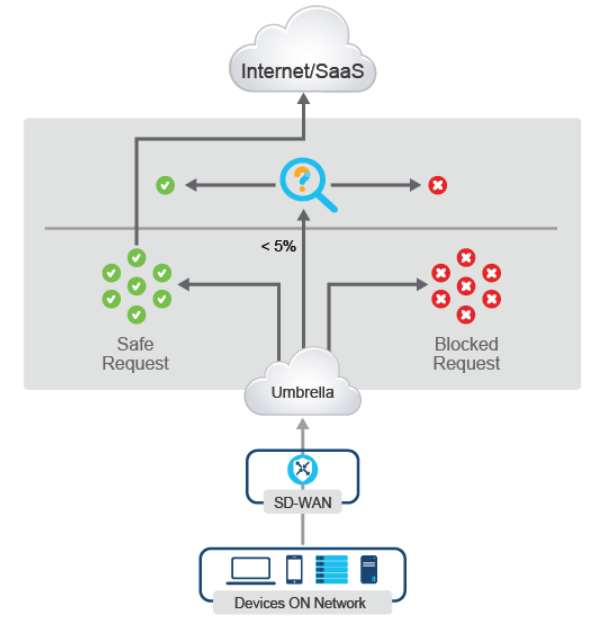
Many sophisticated attacks, for example, malware, ransomware, phishing, and other scams, often use Domain Name System (DNS) to stage the internet infrastructure used to support each stage of their attacks.
These attacks often use:
- DNS tunneling: deliver payloads encoded in DNS queries and responses, exfiltrate data from compromised networks, and execute command and control attacks.
- DNS beaconing: establishing communication with a command-and-control server using only DNS, which is almost always allowed in a network
Cisco Umbrella protects by starting with DNS layer security. Cisco Umbrella proactively blocks requests to malicious destinations before establishing a connection or downloading a malicious file.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.