EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USJuniper Mist Architecture
Juniper Driven by Mist AITM delivers a comprehensive, end-to-end solution to modern networks. In addition, it offers deep insight into wired and wireless networks in traditional architecture.
Mist AI provides a flexible, scalable, distributed architecture with distributed intelligence that maximizes performance, security, and resilience. With the Juniper MistTM cloud, users can access resources, regardless of medium, whether wired or wireless, with consistently high performance, security, and reliability. In addition, users can access their resources from anywhere, whether at headquarters, in a branch office or a remote office, at home, or on the move.
Juniper Mist’s cloud solution features artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning that brings users:
- Predictable, reliable, and measurable network access with comprehensive visibility.
- Network segmentation and security across both wired and wireless infrastructure.
- Location-based services, way-finding, and asset location.
The below figure depicts the Juniper Mist architecture. The Juniper Mist cloud forms the control plane. Juniper Mist provides the benefits of machine learning through microservices running in the cloud. A microservices architecture is a method of developing software applications or functions as a distributed set of independently deployable and manageable modular services.
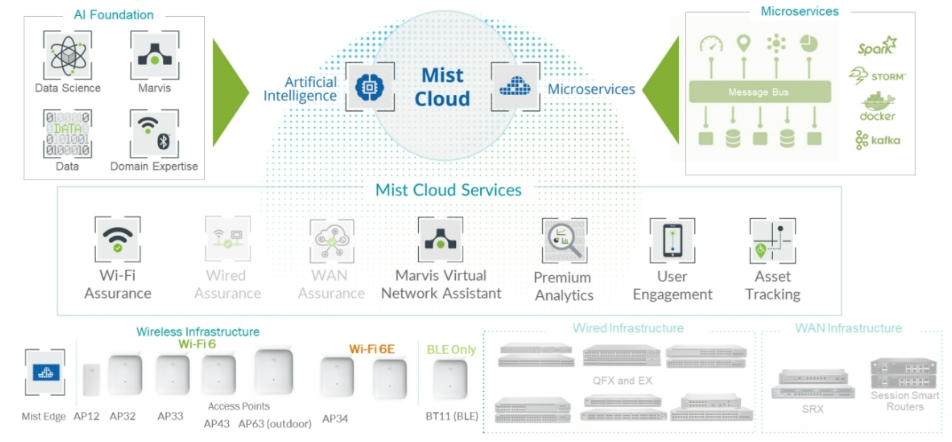
Each service has a unique function that communicates with others through a well-defined mechanism. By leveraging a microservices architecture, the Juniper Mist cloud provides service velocity without disruption and unprecedented elastic scale.
The distributed microservices architecture in the Juniper Mist cloud enables new features and bug fixes to happen with extreme agility—that is, at a pace that far eclipses what is possible with traditional wireless LAN (WLAN) controllers and first-generation cloud architectures. In a Juniper Mist environment, for example, updates typically happen every other week. In contrast, alternative solutions require new updates to take place on scheduled release cycles, which typically occur every few months or longer.
Data Plane Options—Local
All configuration changes are made from the cloud-based UI and sent to the access points (APs). Distributed forwarding on the APs supports the data to be sent locally to its destination rather than involving a controller.
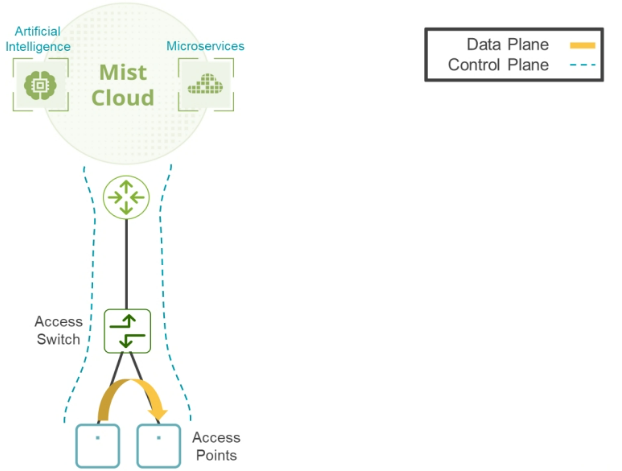
In a centralized controller design, data that must travel through a controller creates a bottleneck and potential single point of failure for a WLAN data plane.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.