EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USWLAN Configuration Options
Multiple SSIDs and BSSIDs
While Juniper Access Points support up to 15 SSIDs per radio, and 1 reserved for mesh, we recommend that you keep the number of SSIDs to a minimum. An AP radio transmits a beacon frame, typically every 102.4 ms, for every SSID enabled at the lowest basic data rate available. Transmitting too many SSID beacons at lower data rates can cause a majority of the airtime being taken up by only beacon frames (beacon overhead). This situation then leaves little airtime for actual client data.
WLAN Configuration Locations
You can create wireless LANs (WLANs) within a configuration template either at the organization level or at the site level.
WLAN Configuration
We map each WLAN to an SSID. This SSID is what a client seeks to establish a connection. A single SSID can broadcast on multiple radio bands. In general, Wi-Fi performance is better on higher bands than lower bands. If you enable multiple Radio Bands on the WLAN, you have to take into account some considerations.
The Radio Band selection process is determined by the client. Modern clients generally prefer higher bands over lower bands. Band steering is a feature that detects whether a connected client has dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) capabilities. This option steers clients with dual-band capability to join the 5-GHz band if the signal is good. Both the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz radios must be enabled on the WLAN. Note that even with band steering, clients can still hear beacon frames from the 2.4-GHz radios and can sometimes connect to these radios. Note that there is no band-steering between 5-GHz and 6-GHz bands. Certain types of clients may experience poor performance because of band steering, which is disabled by default.
VLANs
First, configure a WLAN by going to Site > WLANs and then select Tagged in the VLAN section to configure a static VLAN for your network. Here, you should enter the corresponding VLAN ID and make sure to tag the same VLAN on your switch port. By default, a WLAN will use VLANS–Untagged. Customers may have already deployed VLANs on their network. The VLAN settings enable you to tie a WLAN (SSID) to a specific VLAN.
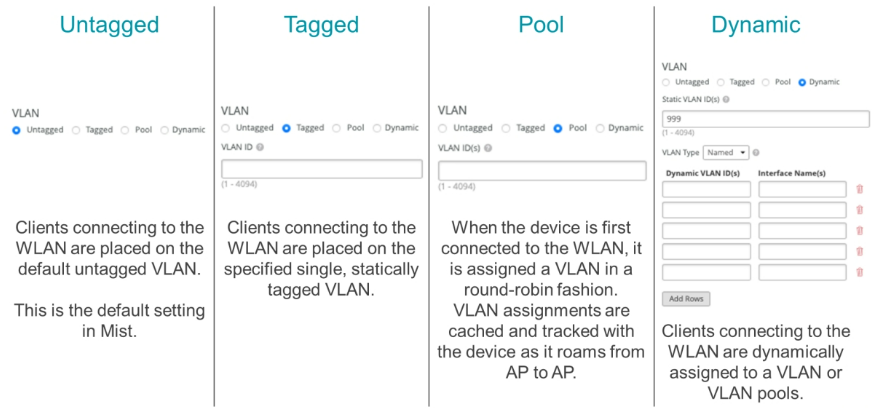
When you enable Pool on your WLAN, the cloud/AP randomly selects VLANs from the VLAN pool and assigns IPs to the clients based on a MAC address hashing algorithm. Using VLAN pools enables the automatic assignment of clients to smaller network segments without requiring a RADIUS server.
When you enable Dynamic on your WLAN, the system assigns clients to different VLANs or VLAN pools, depending on the password they provide when connecting to the SSID. Things you must assign dynamically:
- RADIUS server with the username/password and VLAN assignments configured
- Switch connected to the AP configured with the correct VLANs
Enabling Wi-Fi 6
802.11ax is defined as Wi-Fi 6 in the Juniper MistTM UI. This either turns it on or off on a per WLAN basis. Wi-Fi 6 works across both the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz bands.
The IEEE Standards Board approved the final version of the IEEE 802.11ax standard on February 1, 2021 after getting 95 percent votes in the sponsor ballot for Draft 8 on September 1, 2020. This setting is available in each individual WLAN.
Wireless Traffic Filtering
Wireless traffic filtering enables administrators to filter certain wireless frames.
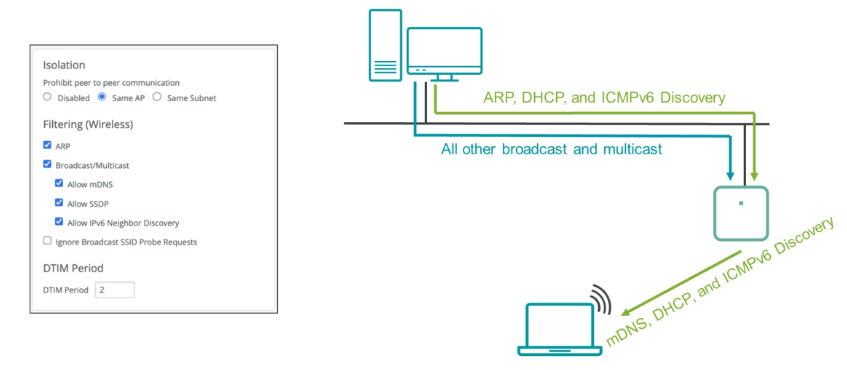
Client Isolation
Client isolation is used to prohibit peer-to-peer communication between wireless clients.
- Disable — Disabling is the default behavior that is automatically set. Communication between clients is accessible and unrestricted.
- Same AP — Regardless of being associated with separate WLAN networks, clients connected to the same AP remain isolated from one another. To use the Same subnet option, make sure the AP is at the correct firmware.
- Same Subnet — It prevents any peer-to-peer traffic from flowing between devices on the same subnet. Make sure clients are configured to receive dynamic IP addresses from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Filter
ARP filter — If you select the ARP filter, the AP blocks all ARP broadcasts from the wired network from going out of the wireless interface. If you do not enable the ARP filter, the wireless interface sends out all unknown ARP requests. By default, the AP responds to ARP requests on behalf of connected clients, regardless of the setting. This setting is called Proxy ARP and is on by default. Disabling Proxy ARP is only possible through the API. We recommend that you enable the ARP filter.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.