EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USPBR Traffic Flow Learning
Depending on the PBR design, several traffic flows are possible. These figures depict the east-west traffic flow between endpoints in EPG client and EPG web, when a firewall service node in Layer 3 mode is integrated in Cisco ACI fabric using a service graph with PBR.
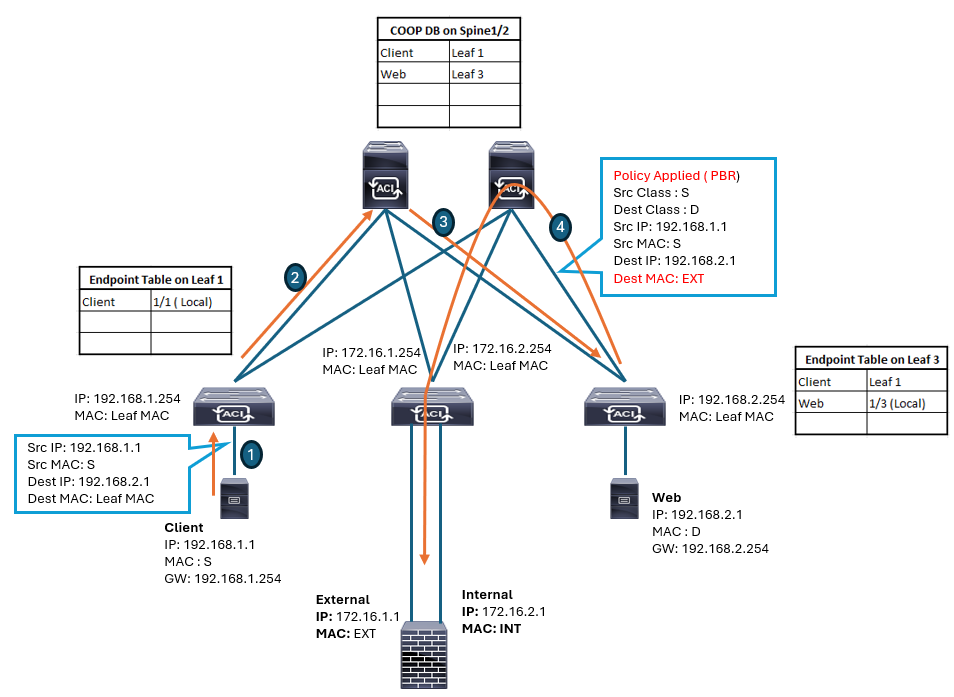 EPG client is a consumer EPG and the EPG web is a provider EPG, using a contract with service graph PBR. The generated traffic from the client endpoint that is destined for the web endpoint follows this sequence:
EPG client is a consumer EPG and the EPG web is a provider EPG, using a contract with service graph PBR. The generated traffic from the client endpoint that is destined for the web endpoint follows this sequence:
-
Endpoint client, which is connected to Leaf 1, sends traffic to the web.
-
Assuming that Leaf 1 has not learned the destination endpoint, Leaf 1 forwards the traffic to the spine proxy. Currently, Leaf1 cannot resolve the destination EPG class ID (pcTag) either to apply a contract with PBR policy.
-
The spine node forwards the traffic to Leaf 3, to which the destination web endpoint is connected. In addition, Leaf 3 learns the source endpoint (client) information from this traffic and populates its endpoint table.
-
Since Leaf 3 can resolve both, the source and destination EPG class IDs, the contract with the PBR service graph is invoked, which results with PBR traffic redirection on Leaf 3. In this process, the destination MAC address is rewritten to the PBR node MAC address (MAC Ext of the firewall external interface) on the consumer side. Leaf 3 looks up the PBR node MAC Ext in the PBR BD. Since Leaf 3 does not know where this destination MAC address is connected, the traffic goes to the spine proxy, which forwards the traffic to Leaf 2, to which the PBR node is connected. Hence, the traffic is forwarded to the external interface of the PBR node for inspection and routing. Leaf 2 does not learn the client IP address from this traffic like Leaf 3 did, because IP data-plane learning is disabled for the PBR node bridge domain.
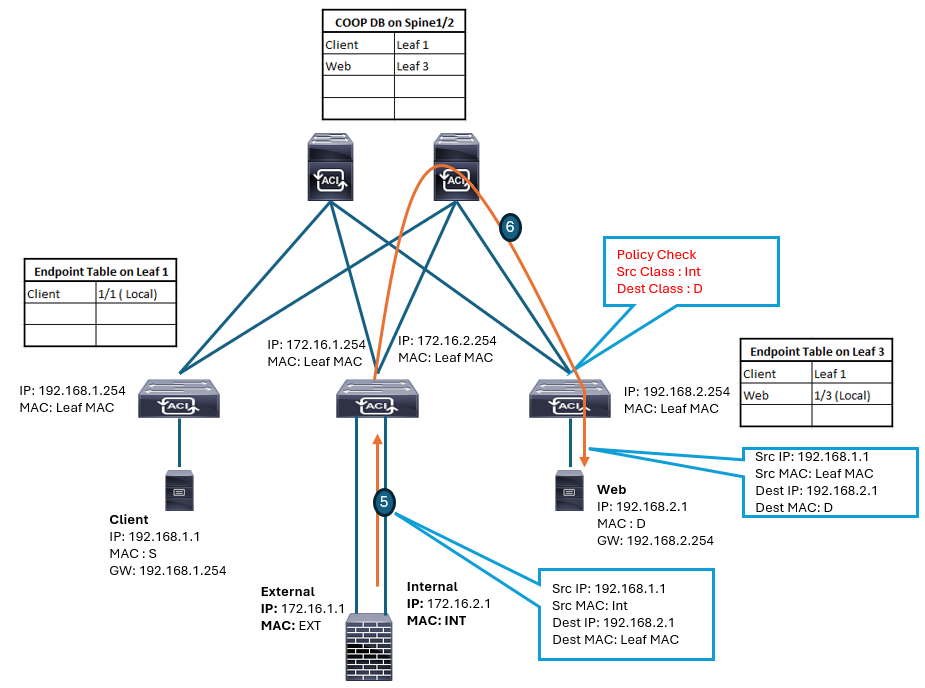
The traffic from the PBR node that is destined for the web endpoint follows this sequence:





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.