EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USRF Waves & RF Maths
RF Waves
Radio frequency (RF) waves are represented as a series of connected, repeating sine waves. This repeating pattern is known as oscillation. The wavelength is the distance between two equivalent points of two adjacent waves (typically the crest, or top). A cycle is the measurement of a single oscillation.
The number of oscillations per second determines the frequency of a wavelength, which is measured in Hertz (Hz), with 1 Hz being one cycle per second. This means that frequency is a measurement of the speed of the oscillation of the wave. Lower frequencies have longer wavelengths and higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths.
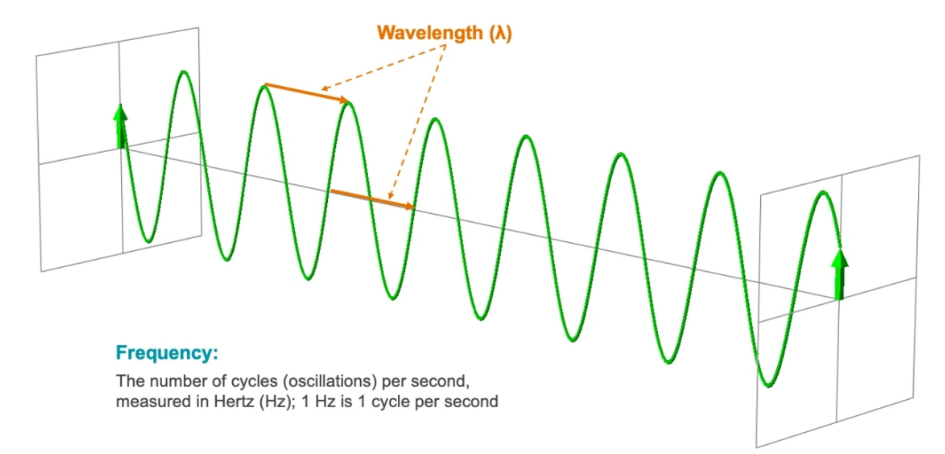
Below figure also shows the RF Units of measure

RF Math
The rule of 10s and 3s:
- If the signal strength increases by 3 dB, the power doubles.
- If the signal strength decreases by 3 dB, the power reduces by half.
- If the signal strength increases by 10 dB, the power increases tenfold, making it 10 times the power.
- If the signal strength decreases by 10 dB, the power decreases tenfold, making it 1/10th the power.

Inverse Square Law
The inverse square law is the mathematical law of how signal power loss occurs after leaving the antenna.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.