EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
US2.4 GHZ WIFI Frequency Bands
2.4-GHz Band (ISM)—22-MHz DSSS Channels
The 802.11 standard defines 14 overlapping channels specified for wireless LAN (WLAN) use in the 2.4-GHz band. Each channel is 22-MHz wide, with a 5 MHz gap between the center frequency of the adjacent channels except for channel 14.
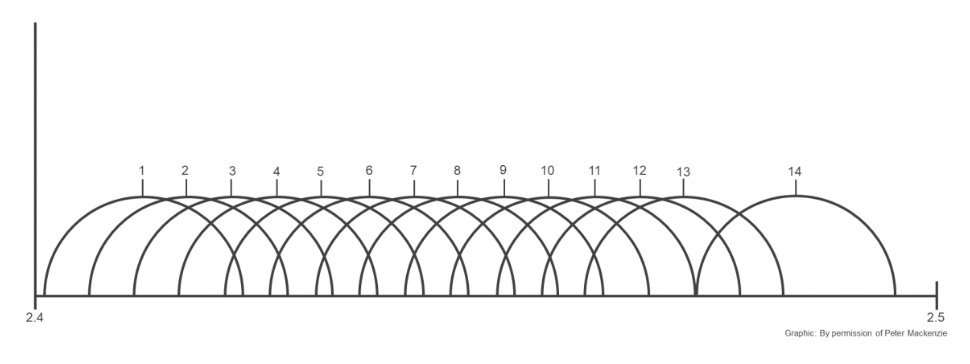
2.4 GHz Band—Nonoverlapping Channels
Direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) channels have a width of 22 MHz and a gap of 5 MHz between their center frequencies. The first three nonoverlapping channels are 1, 6, and 11 and there is 3 MHz of frequency between channels 1 and 6 and channels 6 and 11.
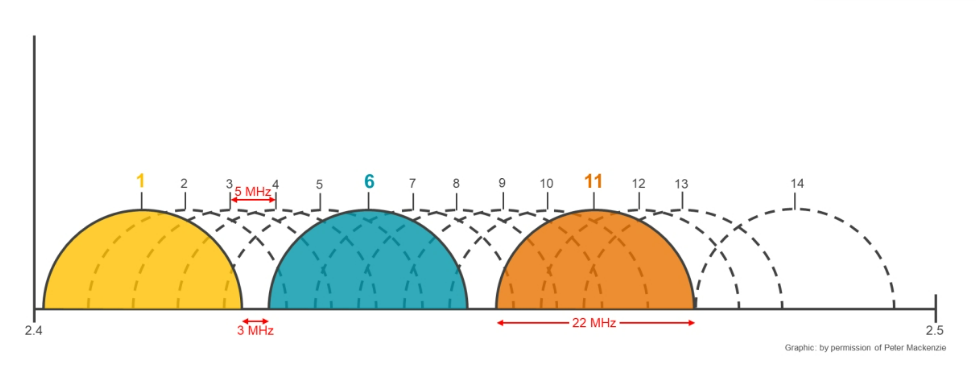
2.4-GHz Adjacent (Overlapping) Channel Interference
WLAN stations operating on overlapping channels within the same airspace cause adjacent channel interference, which can have a destructive effect on WLAN performance.
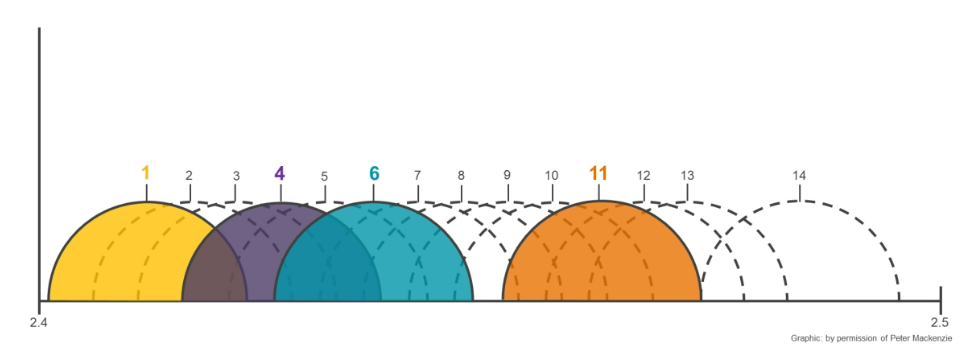
2.4 GHz Three Channel Plan
Because of the negative effects of adjacent channel interface, experts recommend deploying WLANs with a nonoverlapping channel plan.
The amount of 2.4-GHz spectrum that is license-free is different in each regional regulatory domain around the world and therefore the number of channels available also differ.
In the U.S., only the first 11 channels are license-free, as designated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), and therefore channels 1, 6, and 11 are the only three nonoverlapping channels available in the U.S. License-free operation in channels 1 to 13 is acceptable in most countries in Europe. While this enables a variety of three-channel plans, the most universally used and default channel plan used by most vendors' equipment is 1, 6, and 11.
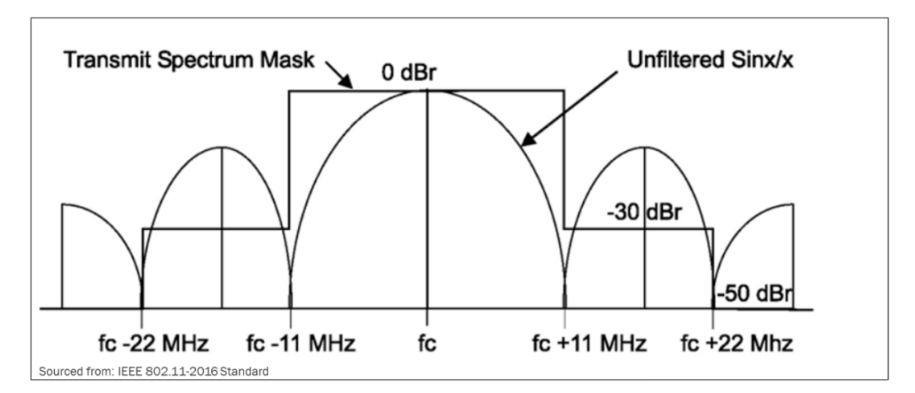
DSSS Spectral Mask
DSSS spectrum mask as defined in the 802.11 standard. With DSSS, data is spread out across the width of a channel. Notice the sidebands on either side of the main 22-MHz wide transmission. These side bands result from the modulation process of DSSS and are important to consider when planning access point (AP) placement.
2.4-GHz Adjacent (Nonoverlapping) Channel Interference
While the 22-MHz wide channels 1, 6, and 11 do not overlap, the sidebands can cause destructive interferences at higher amplitude. We recommend installing colocated APs at least 4 to 5 meters apart.
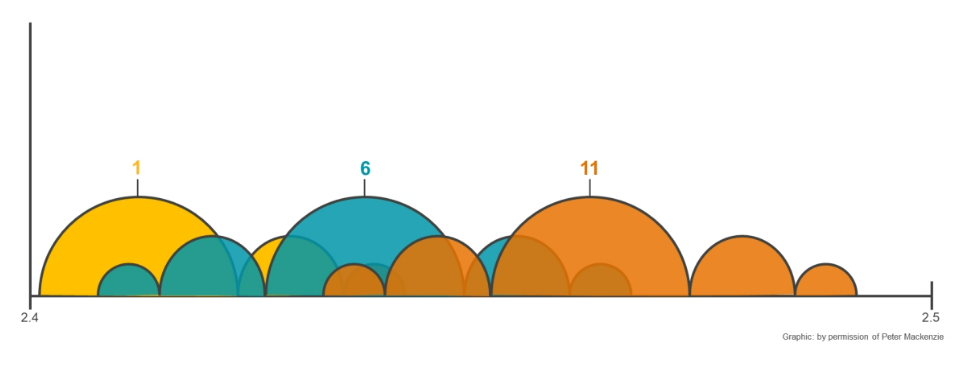
2.4-GHz Co-Channel Contention
When APs are configured for the same channel on the same radio frequency (RF) airspace, the APs and their associated devices share the channel capacity. The channel and physical layer dictate the maximum capacity of a WLAN. Adding another AP on the same channel does not add more capacity but lowers it because of the beacon overhead.
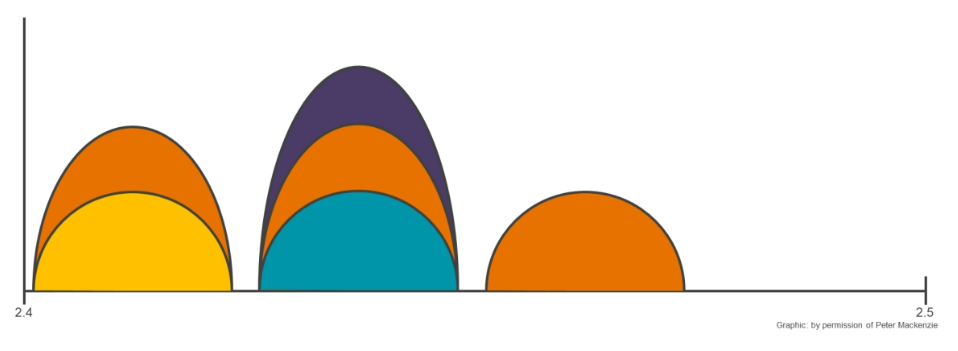
Co-Channel Versus Overlapping Channels
While it is important to minimize co-channel contention (having multiple APs on the same channel), it is even more crucial to avoid overlapping channels as they significantly degrade WLAN performance.
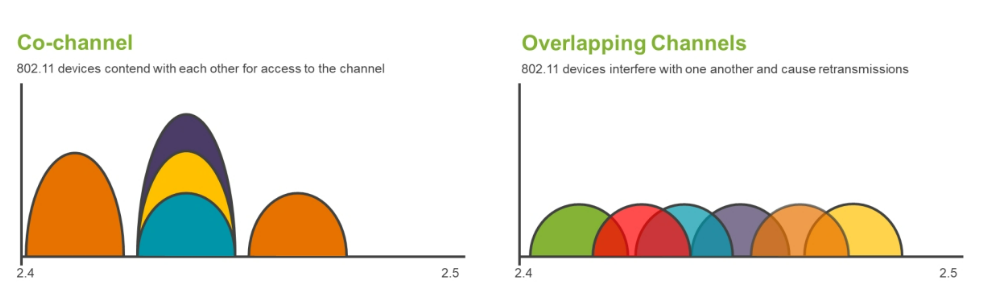
20-MHz OFDM Spectral Mask
The OFDM spectrum mask as defined in the 802.11 standard. Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) was first introduced in the 802.11a amendment as an alternative to DSSS modulation.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.