EMAIL SUPPORT
dclessons@dclessons.comLOCATION
USSD-Access fabric Packet Walk
Cisco SD-Access provides the segmentation capabilities and group-based access control by leveraging existing technologies in a single solution. It is important how these different technologies and protocols affect host onboarding and communication in the SD-Access fabric. This topic will cover a few examples, including initial authentication and authorization during host onboarding, as well as IP address assignment (DHCP), and host registration with the control plane. After the onboarding, the packet flow for unicast traffic between the two hosts in SD-Access will be analyzed.
Host Onboarding—Authentication and Authorization
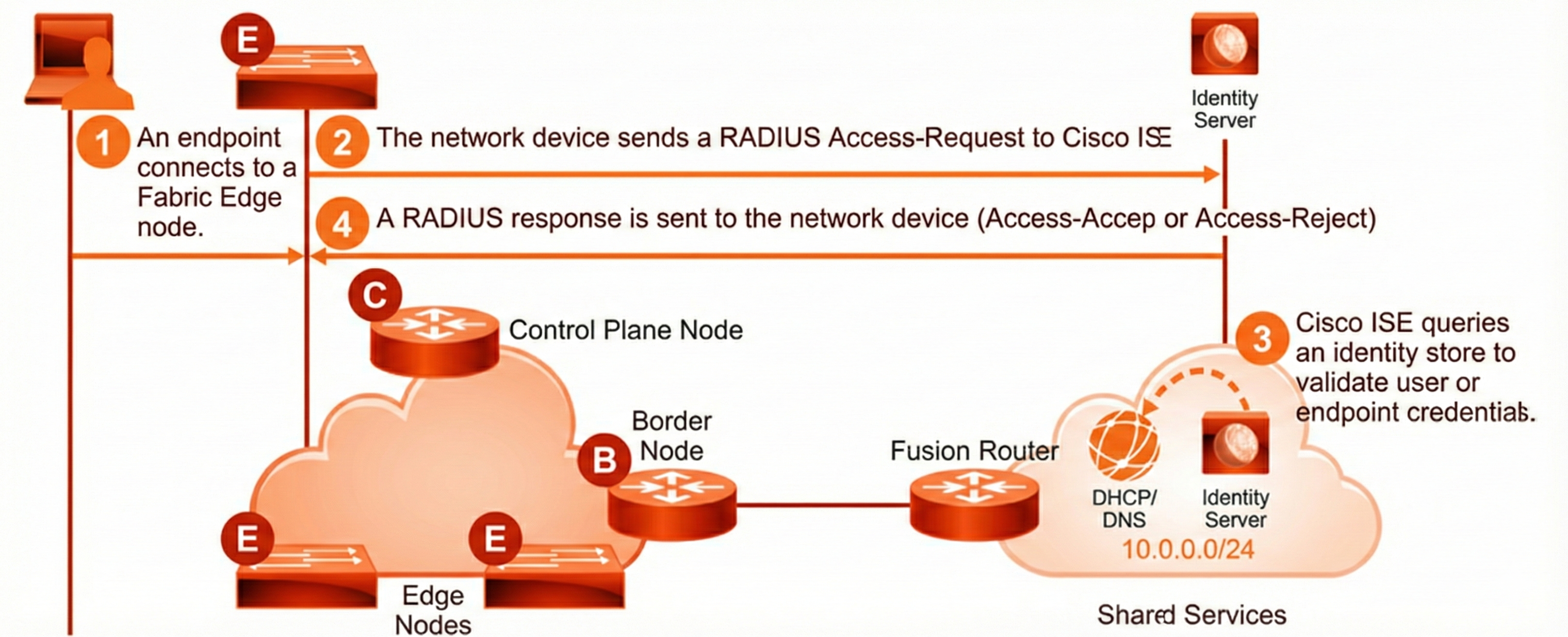
The first step of Host Onboarding in SD-Access is authentication and authorization. This task is most commonly performed by Cisco ISE, but third-party AAA servers are also supported. First, a user or endpoint is authenticated and after successful authentication, the user or endpoint is authorized for network access. Below is a simple flow for Authentication and Authorization. Depending on the authentication methods and protocols being used, the flow can get more complicated.
The user or endpoint will first be authenticated. Only after successful authentication will the user or endpoint be authorized for network access based on the configured policy.
This is an example of a simple authentication and authorization flow:
- The endpoint connects to a fabric edge node. The ports are configured by Cisco DNA Center with the 802.1x authentication.
- The fabric edge node sends a RADIUS Access request to Cisco ISE. The request contains the appropriate RADIUS attributes for the protocol used (PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAPv1, or MS-CHAPv2).
- Cisco ISE uses an identity store, either internal or external, such as Active Directory to validate the user credentials.
- Cisco ISE sends a RADIUS response back to the fabric edge. The response is either an Access-Accept or an Access-Reject, based on authentication results.
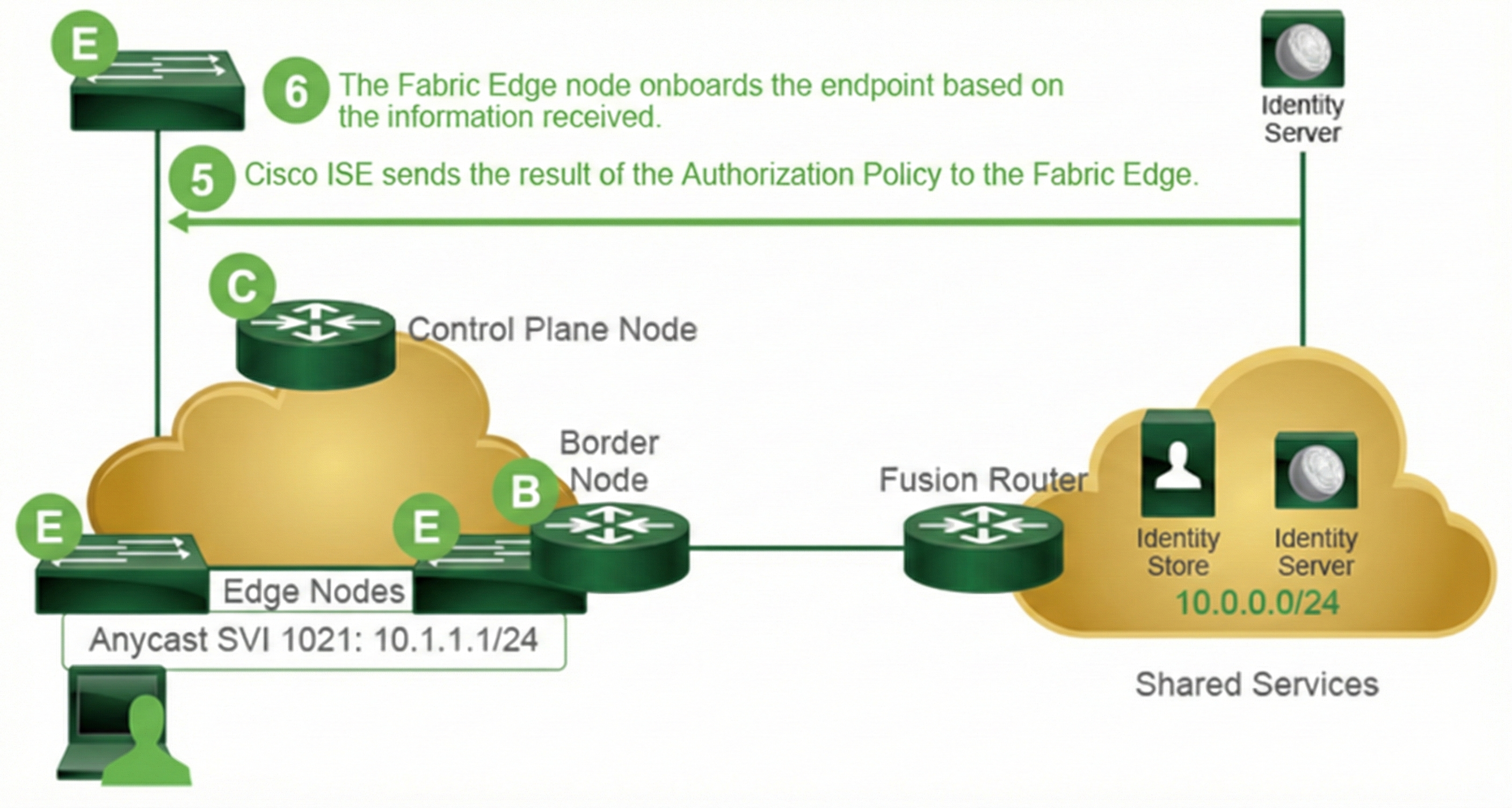
5. If the endpoint or the user is successfully authenticated, Cisco ISE inspects the Authorization policy and sends the results of the matched entry to the fabric edge node.
6. The fabric edge node places the endpoint in the appropriate VLAN based on the information received from Cisco ISE. The fabric edge also assigns an SGT to the user or endpoint and downloads any SGACLs.
This completes Authentication and Authorization. The endpoint must now be assigned an IP address in the appropriate VLAN and get registered within the fabric control plane.
Host Onboarding—DHCP and Endpoint Registration
In SD-Access, DHCP servers are located outside of the fabric network. Each fabric edge node is configured as a DHCP Relay agent. All the fabric edge nodes share the same Anycast Gateway IP address and the fabric relies on the DHCP Option 82 to guarantee the DHCP response is delivered to the appropriate edge node.
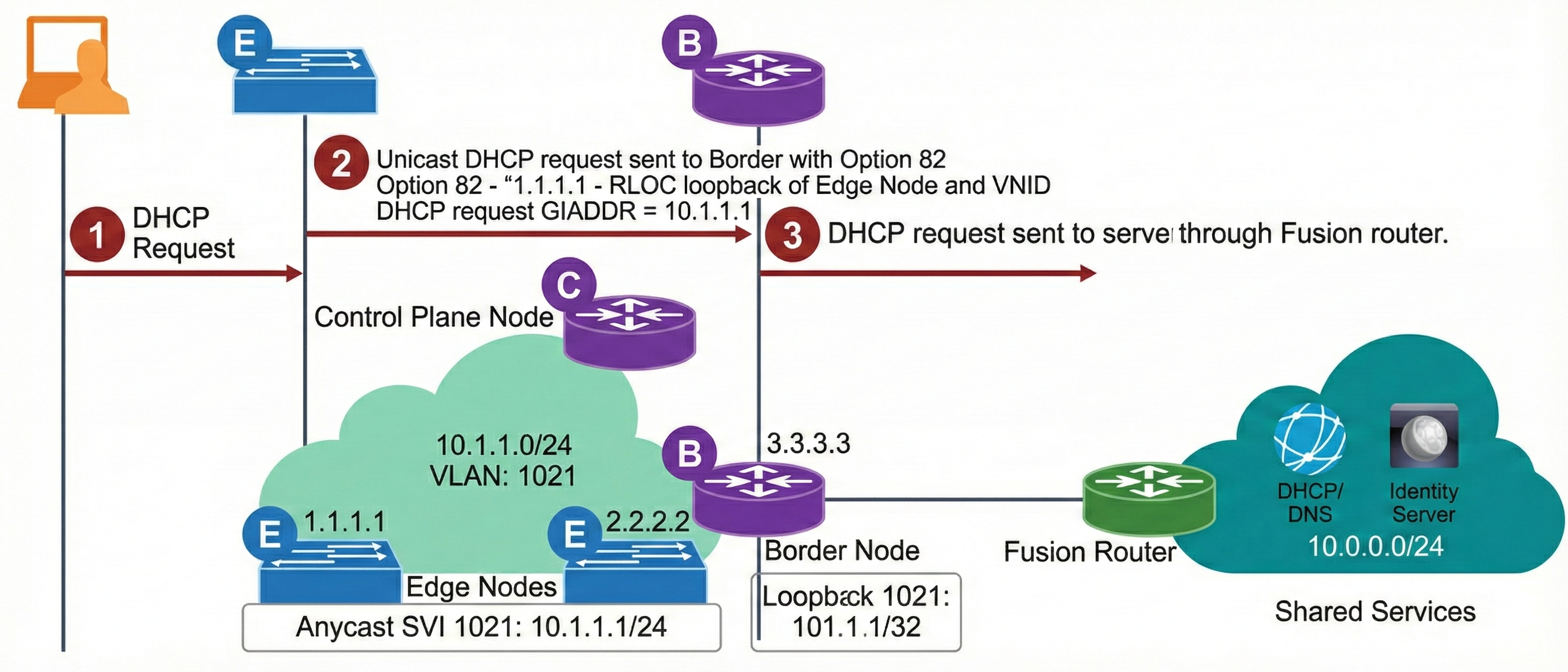
This is an example of the host onboarding process where the endpoint is assigned an IP address using DHCP and is registered with the fabric control plane:
- The endpoint sends a broadcast DHCP request.
- The fabric edge intercepts this broadcast and converts it to a unicast DHCP request with the following parameters:
- GIADDR is set to the Anycast Gateway IP address.
- Option 82 is added with the following DHCP Relay Agent information:
- Agent Circuit ID – identifies the VLAN and interface of the endpoint.
- Agent Remote ID – identifies the L3 VNID and source RLOC.
- The request is then sent to the fabric border for delivery to the DHCP server.
- The fabric border forwards the packet towards the DHCP server outside of the fabric.
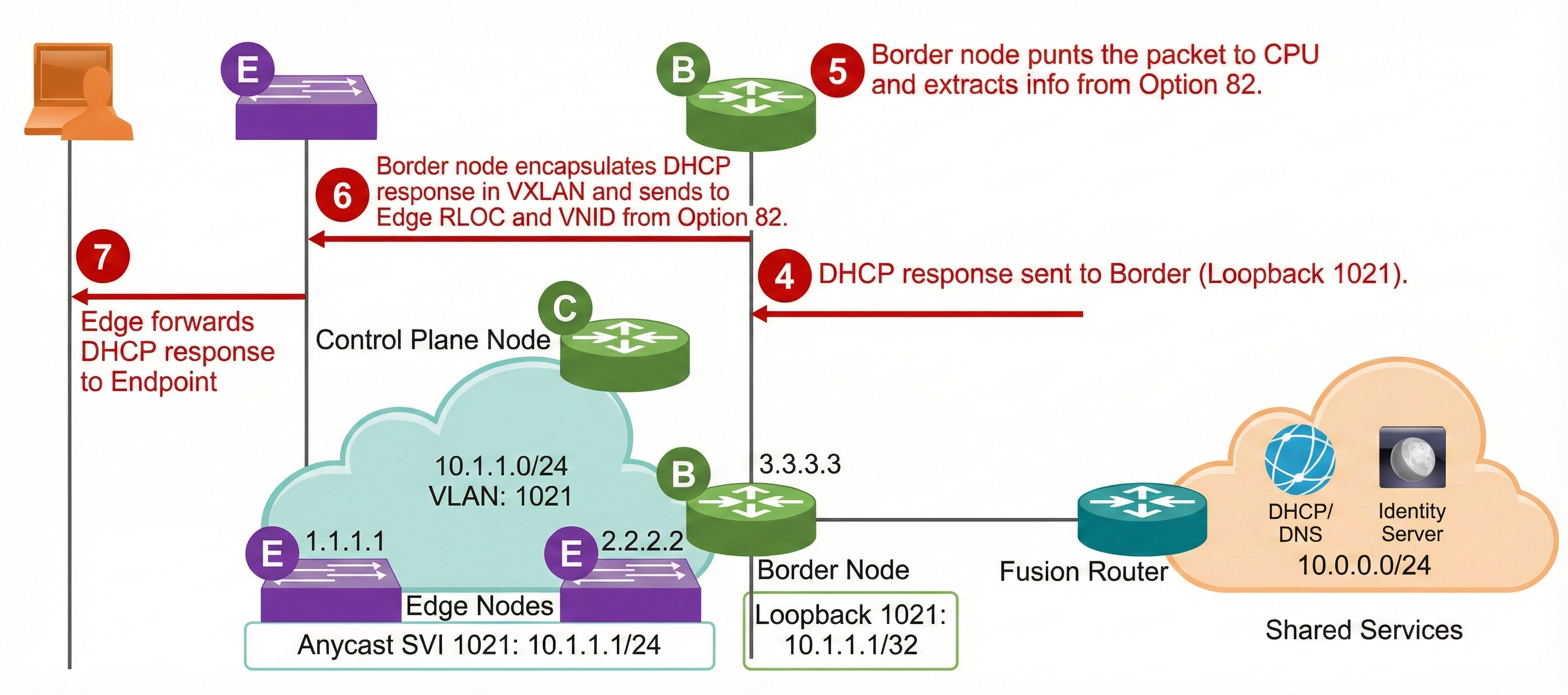
4.The DHCP server sends a response back towards the endpoint with the same Option 82 parameters that were received in the request.
5.The fabric border receives the response, and since it has the same Anycast Gateway IP address assigned on a Loopback interface, it inspects the response and extracts the information from Option 82.
6.The fabric border then encapsulates the packet in VXLAN and forwards it to the appropriate RLOC.
7. The fabric edge receives the DHCP response and forwards it to the endpoint.
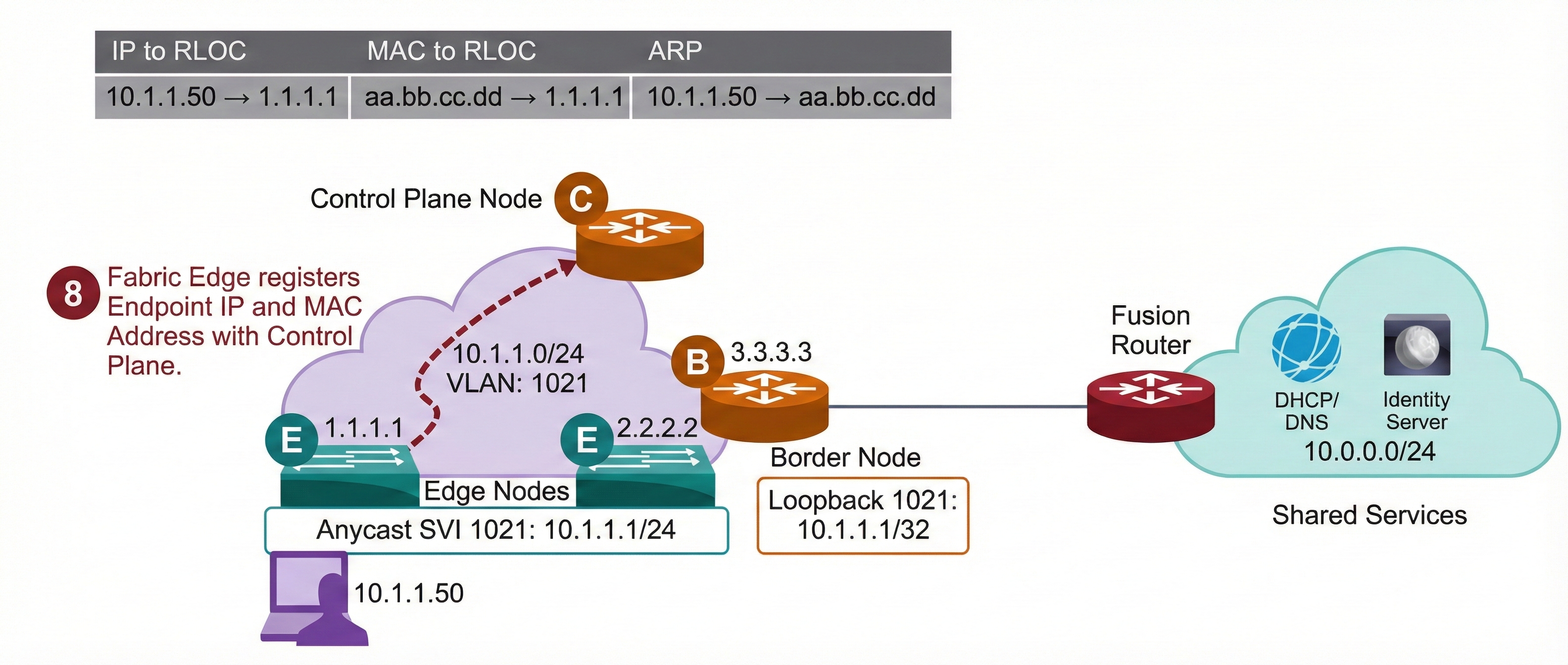
8. Once the endpoint is assigned the address, the fabric edge registers Layer 2 and Layer 3 endpoint information with the Fabric Control Plane.
Unicast Communication—Same Subnet and Different Edge
In SD-Access, users are located in the Endpoint ID (EID) space, which is stretched across the entire fabric. When two users within the fabric wish to communicate, control and data plane protocols are invoked to provide routing information and to deliver the data across the underlay to the remote fabric edge. The following packet flow depicts the process step by step for unicast communication between two endpoints in the same VN connected to two different fabric edge nodes.





LEAVE A COMMENT
Please login here to comment.